Windows 10 is a modern operating system developed by Microsoft Corporation. It is the successor to the 8-year-old Windows 8 OS. As a direct successor of Windows 8, this OS shares a lot more in common with Windows 8 than Windows 7 and previous versions. One of the visible similarities between Windows 10 and 8 is the user interface and theme. Windows 10 is designed to blend modern features with classic ones. It includes some of the most advanced security measures while retaining compatibility with older devices. While its interface may look different than previous versions, it offers more features than ever before. Here are a few reasons why you should upgrade to Windows 10 right now!
Generally, Windows 10 offered users the option to change the options available on the computer making it a very versatile tool for users to access at any time. Even better, the settings on Windows 10 can be easily summoned by the simple shortcut Windows + I option on the keyboard, so, unlike the previously available tool the control panel, settings are not difficult to access. So, such features have brought great usability.
Recommended Post:- How to use Device Encryption in Windows 11
So, here is the list of optional features that you can turn off or on depending on your requirements.
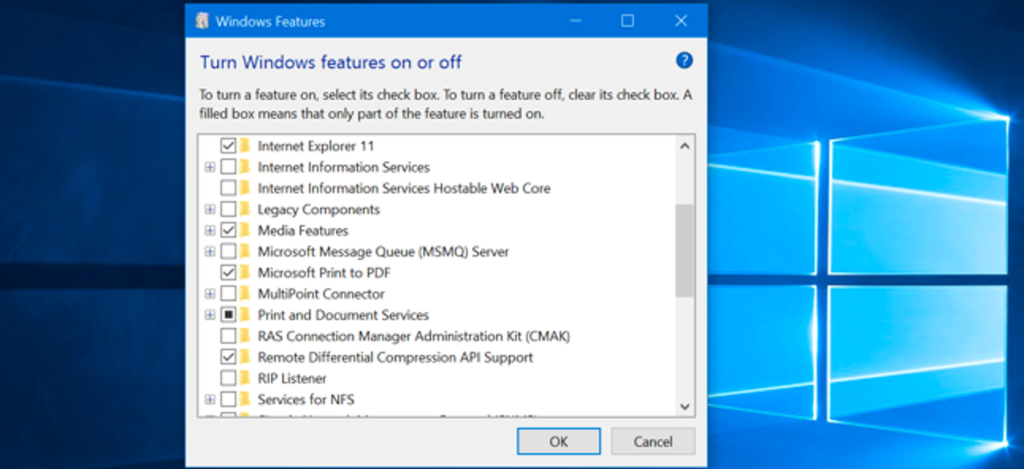
- .NET Framework 3.5 (including .NET 2.0 and 3.0): This feature is essential to running applications created with Microsoft .NET Software Framework version 3.5 or earlier. You can safely enable legacy support, but it’s usually enabled automatically when you need it.
- .NET Framework 4.6 Advanced Services: You must enable this feature for apps built with Framework version 4.6.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Service: Adds Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) support for applications with directories. It is an alternative to Windows Active Directory, a more complex directory solution. This feature is typically required in some corporate network scenarios.
- Containers: Provides services and tools to create and manage Windows Server and Hyper-V containers on the desktop.
- Data Centre Bridging: This feature is an IEEE standard that enables fabric convergence in a data center, where networking, storage, clustering, and traffic management share the same Ethernet network infrastructure. Data center bridging is majorly used in corporate networks.
- Device Lock: You can enable this feature to add services and tools to provide a more controlled experience. Probably, you’ll enable this feature when setting up a kiosk or a temporary device.
- Hyper-V: Microsoft features its own virtualization tech that allows you to create and manage virtual machines on your computer with ease.
- Internet Explorer 11: Even with Windows 10 including Edge, Microsoft continues to include Internet Explorer 11, but it’s possible to disable it if you don’t use it.
- Internet Information Services (IIS): it allows users to set up an FTP server or a server to host websites with management services.
- Internet Information Services Hostable Web Core: This feature Allows you to set an environment to host applications on the web.
- Legacy Components: Windows may add support for older components. This includes DirectPlay, a feature that was part of DirectX.
- Media Features: How to uninstall Windows Media Player in Windows 10.
- Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMO) Server: When generating messages, it queues them instead of sending them so that applications can run correctly over untrusted networks.
- Microsoft Print to PDF: Instead of printing a document on paper, you can print to PDF and save as a PDF file. You can disable this feature if you don’t need it or use it.
- MultiPoint Connector: If this feature is enabled, you will be able to monitor and manage your computer using a MultiPoint Manager
- Print and Document Services: This feature allows users to use printing services on Windows. Here you can enable or disable network scanning, faxing, and printing services.
- RAS Connection Manager Administration Kit (CMAK): You can use CHMAK to create custom profiles for connecting to Remote Access servers.
- Remote Differential Compression API Support: Provides a synchronization algorithm that intelligently compares the two files you want to sync and only updates the differences. Only certain programs can use this feature.
- RIP listener: If you are on a network that uses the older RIP version 1 protocol, you can use a RIP listener to receive RIP updates over the network. If you’re on your home network, you’re probably not using it.
- Services for NFS: This feature permits you to access files using the Network File System (NFS) protocol.
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP): This allows the SNMP agent on your computer to monitor and report to the network console switches, routers, and other devices on your network.
- Simple TCPIP Services: Provides support for additional TCP/IP protocol services, including “Echo”, “Character Generator”, “Daytime”, “Discard”, and “Quote of the Day (QUOTE)”.
- SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support: Provides support to configure file and printer sharing for previous versions of the OS, including Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 R2.
- SMB Direct: Allows the use of network adapters with Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) capability to improve file sharing feature using SMB 3.x.
- Telnet Client: This is a command-line utility that allows users to connect to other computers or devices, such as routers and switches that are running a telnet server.
- TFTP Client: This is a command line tool that can be used to upload and download files using the Trivial File Transfer Protocol. This protocol is insecure and should only be used if necessary.
- Windows Identity Foundation 3.5: New applications use .NET 4, which adds a new identity framework, but applications written using older .NET technologies may need this feature.
- Windows PowerShell 2.0: PowerShell is a powerful command line scripting tool that is pretty similar to Command Prompt. PowerShell is enabled by default, but you can disable this feature in Windows 10.
- Windows Process Activation Service: This feature Installs services that may be needed when using IIS web services.
- Windows Subsystem for Linux (Beta): Install the Ubuntu Bash shell command line tool on Windows 10. However, additional steps must be followed to complete the installation.
- Windows TIFF iFilter: When enabled, Windows 10 can index and search the Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) using Optical Character Recognition (OCR), but it typically uses more system resources than traditional file indexing and searching. However, when you work with these types of documents, it can help you find these scanned documents faster.
- Work Folders Client: Allows file synchronization with network file servers.
- XPS: This is a legacy Microsoft file format that resembles a PDF file. You can also print the document to XPS, but the PDF format is more common. If you don’t want to use it, you can delete it by deselecting it.
- XPS Viewer: This is the application that Microsoft has included in the operating system for opening XPS files. You can safely disable this feature if it does not work with any XPS files.
Simple Steps to Turn On or Off the Windows Features
- To turn on or off the Windows Features, open the search option by using the Windows + S key on the keyboard.
- Here, search for Turn Windows Feature on or off and then select the relevant option from the search results.
- Here, you will find the toggle buttons that you can select or deselect toggle button to enable or disable the feature on your computer.
Hope the information provided above was helpful and informative, with these simple steps you can easily enable or disable the features on Windows computers.