TLS is a security technology that lets you secure computer networking by protecting data privacy and security. It superseded SSL in prior Windows versions and authenticates and encrypts data transferred over HTTPS via a TLS handshake.

The TLS protocol is critical for ensuring the security of your online activities, and enabling new TLS versions such as TLS 1.3 on your Windows 11 PC is required. Because older TLS protocols, such as TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1, are less trustworthy, you may need to disable them, especially if you are enabling the most recent protocols. This article will demonstrate how to enable or disable TLS settings on Windows 11.
The Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol, which offers security for Internet communications such as Web browsing, email, and instant messaging, is available in two versions: TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1.
Given that attackers are always discovering new methods of attack, various vulnerabilities in earlier versions of TLS have been discovered that can allow attackers to decrypt your data. However, here’s how to activate either in Windows 11.
Recommended Post:- Fixed: The Network Security Key isn’t Correct on Windows
What is the Distinction Between TLS 1.0 and 1.1?
The two most extensively used versions of the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol are TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1. Both versions provide a comparable level of security and encryption. However, there are certain distinctions between them that customers should be aware of while deciding between them:
- Security: There is minimal difference between these two protocols in terms of security: both are still deemed secure, but some may consider them obsolete and favor newer versions such as TLS 1.2 or even 1.3 (which is not yet supported by many browsers).
- Speed: TLS 1.1 is faster than TLS 1.0 because it requires fewer CPU cycles to process.
- Difficulty in upgrading: Due to a lack of resources or compatibility difficulties with their operating systems, certain older client programmes may be unable to handle newer versions of the protocol.
Difference Between SSL and TLS
SSL is an abbreviation for Secure Socket Layer, whereas TLS is an abbreviation for Transport Layer Security. The protocols used to ensure security between web browsers and web servers are Secure Socket Layer and Transport Layer Security.
The primary distinction between Secure Socket Layer and Transport Layer Security is that in an SSL (Secure Socket Layer), the message digest is utilized to generate a master secret, and it provides the core security services of authentication and confidentiality. TLS (Transport Layer Security) uses a pseudo-random method to generate a master secret.
SSL and TLS are cryptographic protocols used for authentication and data encryption between networked servers, computers, and devices. SSL has been around for 25 years. Netscape created the initial version of SSL (version 1.0) in 1995, however, it was never published due to serious security flaws. SSL 2.0 was a failure, and SSL 3.0 was released slightly over a year later. People contributed to the development of TLS 1.0 in unison. TLS 1.0 is fairly similar to SSL 3.0, but there are enough differences to classify it as SSL 3.0 ahead of time.
The fundamental distinctions between SSL and TLS will be discussed in this section.
- SSL stands for secure socket layer, whereas TSL stands for transportation layer protection.
- The cryptographic protocols SSL and TLS authenticate server-to-device data exchanges. A cryptographic protocol, for example, encrypts data transmitted between a Web server and a user.
- To encrypt the data from both ends, a secure framework is required. This is supported with an SSL/TLS certificate. It acts as an encryption portal for encrypting data, preventing hackers from gaining illegal access.
- Even though the TLS model relies on the authentication code for the HMAC hash, key information and configuration data are required on an ad hoc basis for SSL message authentication.
- SSL was a groundbreaking cryptographic protocol. TLS, on the other hand, was the most recently modified SSL version.
In Windows 11, How Can You Enable TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1?
Let’s take a closer look at how to enable TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 on your Windows 11 PC.
Solution 1: Enabling TLS 1.0 in the System
1. Use the Control Panel to enable TLS 1.0 1.1
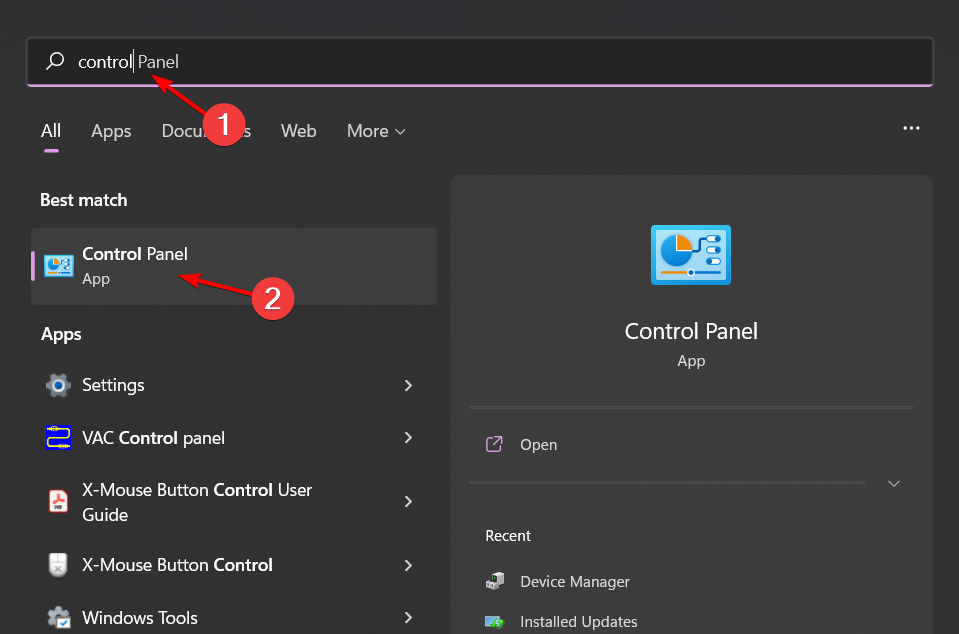
- Step 1: Press the Windows key, type Control Panel into the search field, and then press the Open button.
- Step 2: Navigate to Network and Internet.
- Step 3: Select Internet Options.
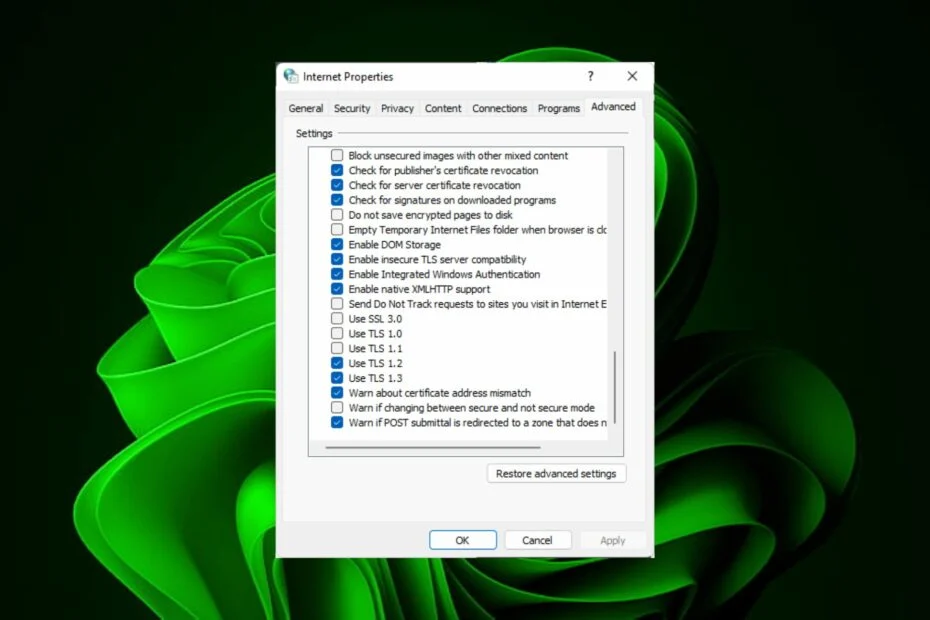
- Step 4: In the resulting Internet Properties dialogue box, select the Advanced tab.
- Step 5: Scroll down and select the box next to Use TLS 1.0 under Settings, then click the Apply and OK buttons to save your changes.
1.2 Execute the Run command.
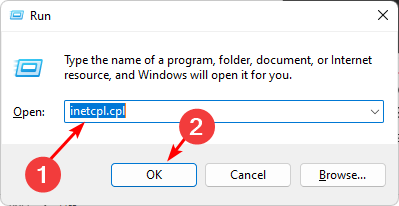
- Step 1: Press the Windows + R keys together to launch the Run command.
- Step 2: In the dialogue box, type inetcpl.cpl and press Enter.
- Step 3: In the Internet Properties box that appears, navigate to the Advanced tab.
- Step 4: Scroll down to Settings and select the box next to Use TLS 1.0 before clicking the Apply and OK buttons to save your changes.
Solution 2: Enabling TLS 1.1 in the System
2.1 Make use of the Control Panel
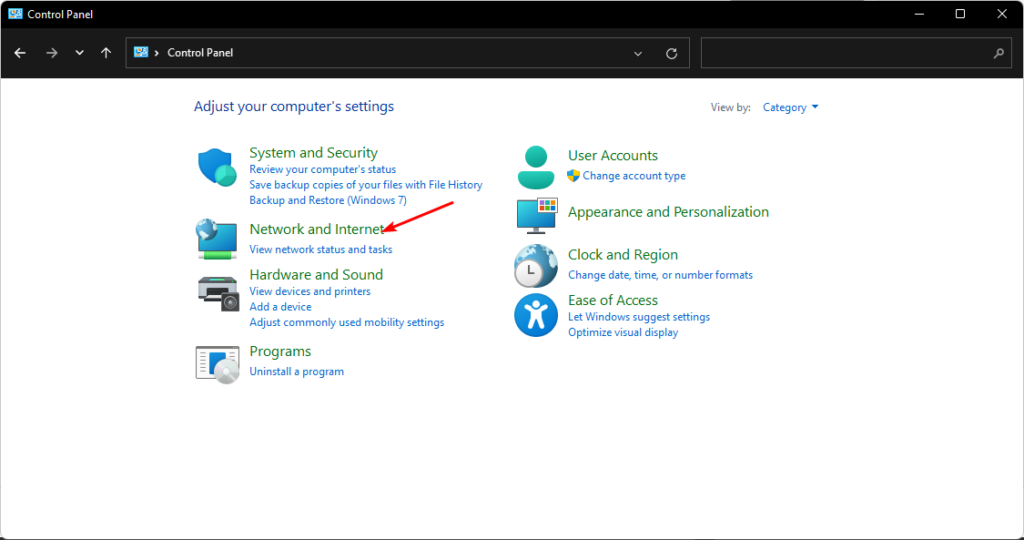
- Step 1: Press the Windows key, type Control Panel into the search field, and then press the Open button.
- Step 2: Navigate to Network and Internet.
- Step 3: Select Internet Options.
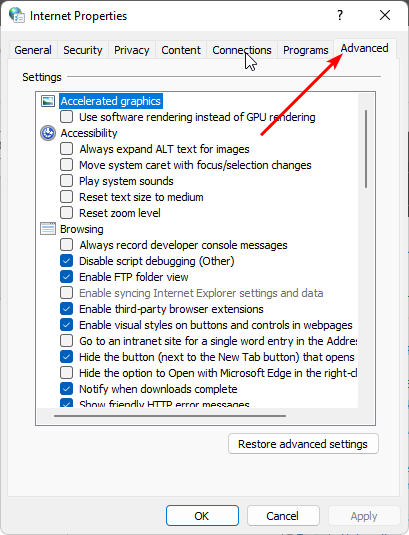
- Step 4: In the resulting Internet Properties dialogue box, select the Advanced tab.
- Step 5: Scroll down and select the box next to Use TLS 1.1 under Settings, then click the Apply and OK buttons to save your changes.
1.2 Execute the Run command.
- Step 1: Press the Windows + R keys together to launch the Run command.
- Step 2: In the dialogue box, type inetcpl.cpl and press Enter.
- Step 3: In the Internet Properties box that appears, navigate to the Advanced tab.
- Step 4: Scroll down and select the box next to Use TLS 1.1 under Settings, then click the Apply and OK buttons to save your changes.
Conclusion
Although the TLS 1.0 and 1.1 protocols can still be enabled, it is crucial to highlight that they are no longer supported by most browsers and cannot be trusted to deliver secure communications.
Depending on the browser you’re running, you can also activate TLS support. To that end, we’ve compiled a list of browsers that support the most recent TLS versions. If you encounter a TLS error, get connected with the Microsoft support team.
TLS helps safeguard your data and prevents unauthorized third parties from accessing it. This security is, however, more ensured in the newer TLS 1.3 than in the earlier TLS 1.0. TLS 1.3 should be enabled and TLS 1.0 should be disabled on your Windows 11 PC.